GLP-1 Sema
$ 39.00 – $ 99.00Price range: $ 39.00 through $ 99.00
All products are for laboratory research purposes only. Not for human consumption, medical, or veterinary use. Novara Peptides does not condone or support the use of peptides outside of controlled scientific research. By purchasing, you acknowledge that you are a qualified researcher or institution. You must be 21 or older.




GLP-1S (Research Compound)
Tagline: Advanced GLP-1 Analogue
Product Description
GLP-1S is a synthetic analogue of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), designed for laboratory and scientific research only. Researchers study this compound for its unique role in metabolism regulation, insulin signaling, and cardiovascular pathways. Due to its high stability and structural similarity to endogenous GLP-1, GLP-1S offers consistent results in controlled experimental environments.
This compound is not intended for human use, treatment, or diagnostic purposes. All applications must remain strictly within research settings.
Why Researchers Choose GLP-1S
High purity for reproducible results
Strong stability under proper storage conditions
Reliable solubility for precise dosing in experiments
Widely studied in metabolic and cardiovascular research models
Easy to handle and reconstitute for laboratory protocols
Important Note
For laboratory and scientific research only. Not for human consumption.Semaglutide
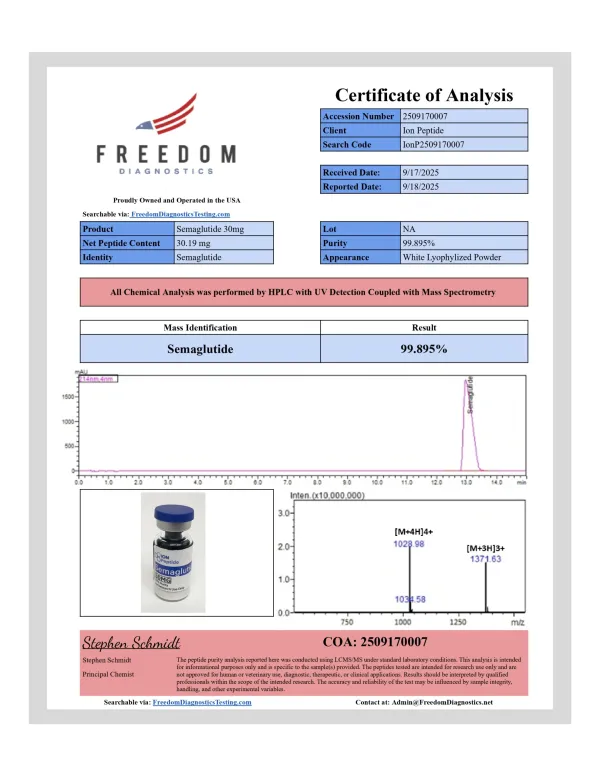
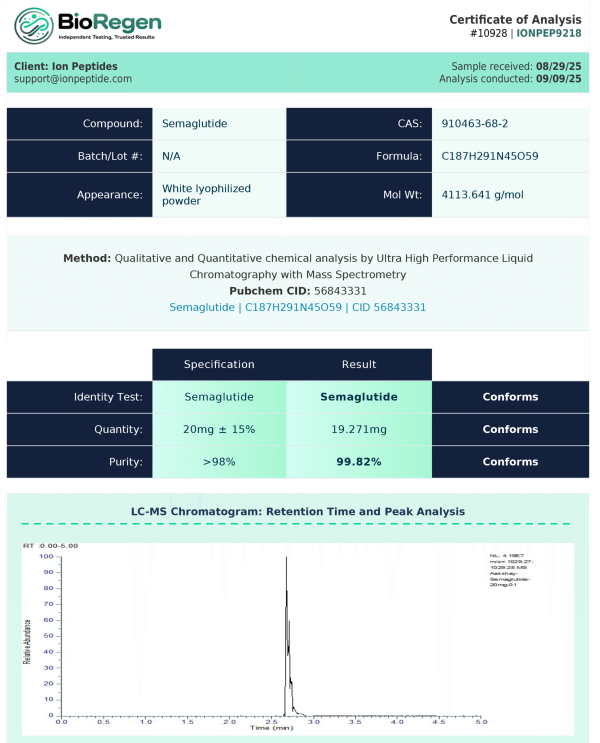
| Specification | Information |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | C187H291N45O59 |
| Molecular Mass | ~4113 g/mol |
| CAS Number | 910463-68-2 |
| Form | Lyophilized powder |
| Shelf Life | Up to 24 months (lyophilized) |
| Intended Use | Laboratory research only |
| Storage | –20°C (lyophilized), –80°C after reconstitution |
Research
Metabolism & Insulin Sensitivity
GLP-1S is commonly studied for its effects on glucose metabolism and insulin regulation. Research indicates that GLP-1 analogues may influence beta-cell activity and insulin secretion in animal and cell models [1].
Cardiovascular Function
Studies explore the compound’s role in cardiovascular health, particularly in how GLP-1 receptor activity may impact blood pressure regulation and vascular inflammation [2].
Appetite & Energy Balance
Experimental data suggest that GLP-1S can influence hypothalamic signaling pathways, affecting food intake and energy expenditure in controlled studies [3].
Neuroprotection & Cognitive Health
Preclinical findings indicate potential roles for GLP-1 analogues in neuroprotection and memory pathways, though mechanisms are still under investigation [4].
References
Holst JJ (2007). The physiology of glucagon-like peptide 1. Physiol Rev. https://journals.physiology.org/doi/pdf/10.1152/physrev.00034.2006
Nauck MA, Quast DR, Wefers J, Meier JJ (2021). GLP-1 receptor agonists in cardiovascular outcomes: state-of-the-art. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.
https://europepmc.org/article/MED/34181914van Can J, Sloth B, Jensen CB, Flint A, Blaak EE, Saris WH (2014). Effects of the once-daily GLP-1 analog liraglutide on gastric emptying, glycemic parameters, appetite, and energy metabolism in obese, non-diabetic adults. Diabetes Obes Metab.
https://europepmc.org/articles/PMC4052428Hölscher C (2019). Central effects of GLP-1: new opportunities for treatments of neurodegenerative diseases. Prog Brain Res.
https://europepmc.org/article/MED/23999914Drucker DJ (2018). “Mechanisms of action and therapeutic application of GLP-1 analogues.” Cell Metabolism.
https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/fulltext/S1550-4131%2818%2930179-7
Mechanism of Action (How GLP-1S Works)
Mimics endogenous GLP-1 structure, binding to GLP-1 receptors [1].
Activates signaling cascades that regulate insulin release and glucose metabolism [2].
Slows gastric emptying, influencing appetite regulation in experimental models [3].
Enhances cellular energy balance through AMPK and related pathways [4].
Modulates inflammation and oxidative stress in preclinical systems [5].
References
Holst JJ (2007). The physiology of glucagon-like peptide 1. Physiol Rev. https://journals.physiology.org/doi/pdf/10.1152/physrev.00034.2006
Nauck MA, Quast DR, Wefers J, Meier JJ (2021). GLP-1 receptor agonists in cardiovascular outcomes: state-of-the-art. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.
https://europepmc.org/article/MED/34181914van Can J, Sloth B, Jensen CB, Flint A, Blaak EE, Saris WH (2014). Effects of the once-daily GLP-1 analog liraglutide on gastric emptying, glycemic parameters, appetite, and energy metabolism in obese, non-diabetic adults. Diabetes Obes Metab.
https://europepmc.org/articles/PMC4052428Hölscher C (2019). Central effects of GLP-1: new opportunities for treatments of neurodegenerative diseases. Prog Brain Res.
https://europepmc.org/article/MED/23999914Drucker DJ (2018). “Mechanisms of action and therapeutic application of GLP-1 analogues.” Cell Metabolism.
https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/fulltext/S1550-4131%2818%2930179-7
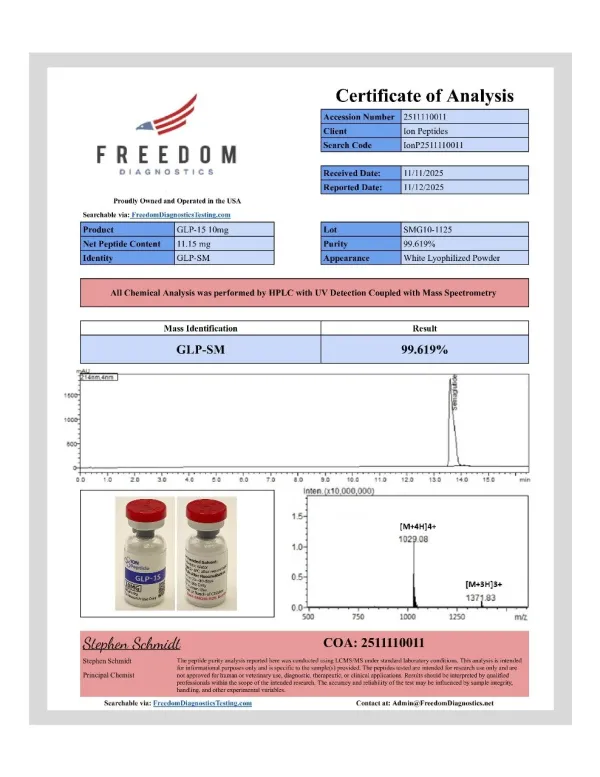
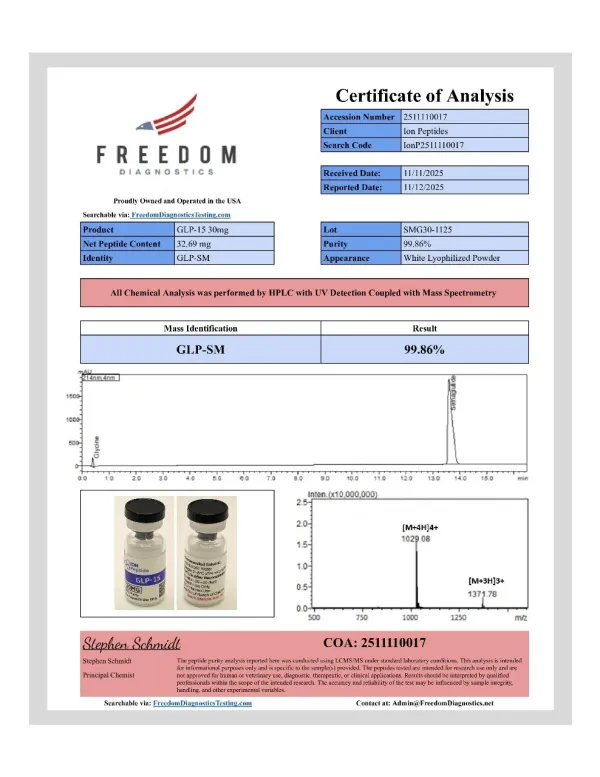
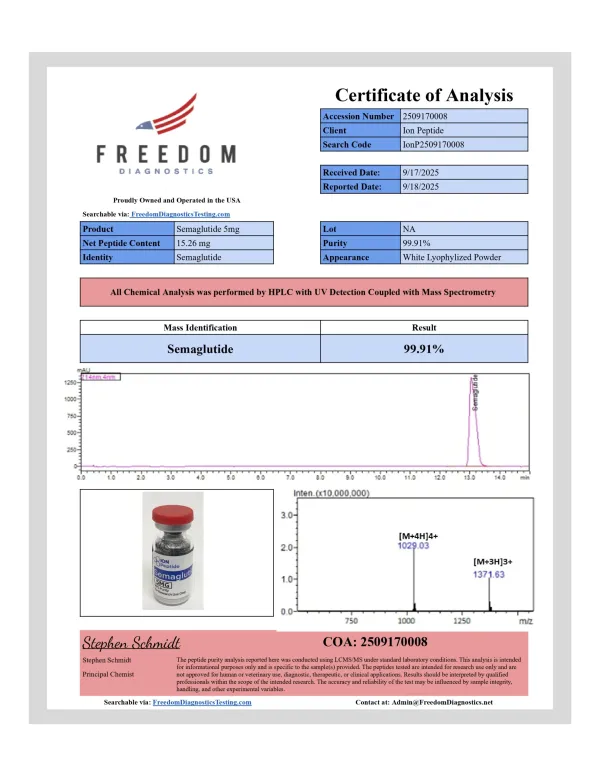
Related products
-
Cagrilintide
$ 49.00 – $ 79.00Price range: $ 49.00 through $ 79.00 Select options This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page